Multi-factor authentication is a process where a user is prompted during the sign-in process for an additional form of identification, such as to enter a code on their cellphone or to provide a fingerprint scan.
If you only use a password to authenticate a user, it leaves an insecure vector for attack. If the password is weak or has been exposed elsewhere, is it really the user signing in with the username and password, or is it an attacker? When you require a second form of authentication, security is increased as this additional factor isn't something that's easy for an attacker to obtain or duplicate.

Azure Multi-Factor Authentication works by requiring two or more of the following authentication methods:
Something you know, typically a password.
Something you have, such as a trusted device that is not easily duplicated, like a phone or hardware key.
Something you are - biometrics like a fingerprint or face scan.
Users can register themselves for both self-service password reset and Azure Multi-Factor Authentication in one step to simplify the on-boarding experience. Administrators can define what forms of secondary authentication can be used. Azure Multi-Factor Authentication can also be required when users perform a self-service password reset to further secure that process.

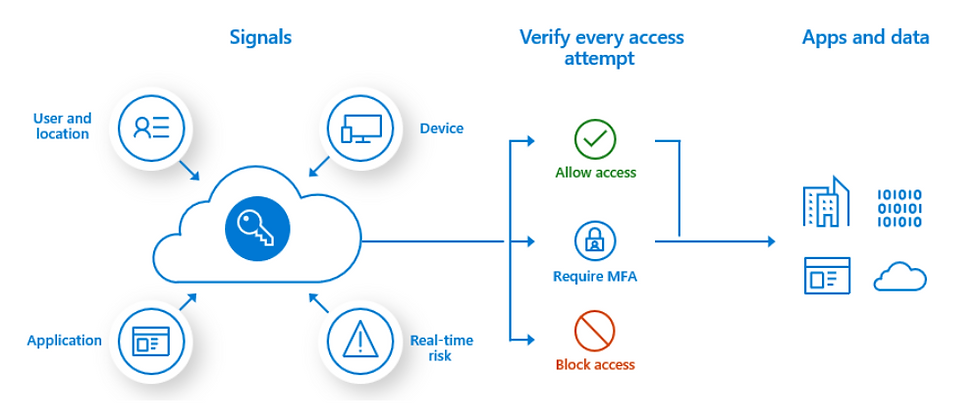
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication helps safeguard access to data and applications while maintaining simplicity for users. It provides additional security by requiring a second form of authentication and delivers strong authentication via a range of easy to use authentication methods. Users may or may not be challenged for MFA based on configuration decisions that an administrator makes.
Your applications or services don't need to make any changes to use Azure Multi-Factor Authentication. The verification prompts are part of the Azure AD sign-in event, which automatically requests and processes the MFA challenge when required.
Available verification methods
When a user signs in to an application or service and receive an MFA prompt, they can choose from one of their registered forms of additional verification. An administrator could require registration of these Azure Multi-Factor Authentication verification methods, or the user can access their own My Profile to edit or add verification methods.
The following additional forms of verification can be used with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication:
Microsoft Authenticator app
OATH Hardware token
SMS
Voice call
How to enable and use Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Users and groups can be enabled for Azure Multi-Factor Authentication to prompt for additional verification during the sign-in event. Security defaults are available for all Azure AD tenants to quickly enable the use of the Microsoft Authenticator app for all users.
For more granular controls, Conditional Access policies can be used to define events or applications that require MFA. These policies can allow regular sign-in events when the user is on the corporate network or a registered device, but prompt for additional verification factors when remote or on a personal device.


Comments